Digital Distribution Model Dial
How can digitalization be used to innovate my distribution?TIAS professor of Strategic Leadership Ron Meyer presents an insightful tool to kickstart your thinking: Digital Distribution Model Dial.
Key Definitions
Distribution is the process of getting a product/service from the producer to its end user. This transferring from creator of the product/service to its consumer involves changing hands (the distribution channel) and changing location (the distribution logistics). The distribution channel can be direct from producer to user, or indirect, via one or more intermediaries. The distribution logistics involves bridging the physical distance by transportation and storage.
Digital technologies have the impact of making things more intangible, more connected, and more intelligent. As such, they can be employed to innovate the way companies organize their distribution channels and the distribution logistics – their distribution model.
Conceptual Model
The Digital Distribution Model Dial is one of the three dials (see below right) that can be turned to create an innovative value proposition. The Revenue Model Dial was discussed in Meyer’s Management Models #4 and The Digital Product Model Dial as #19. The Digital Distribution Model Dial suggests that there is no fixed set of distribution models from which to choose, but that reinvention can be sought along four different dimensions (two channel dimensions and two logistics dimensions), separately or at the same time. Each dimension has been formulated as a question, with several common examples mentioned as options to consider.
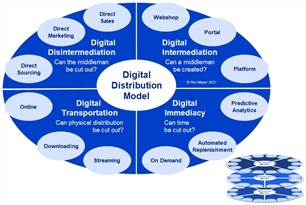
Download picture
Key Elements
The four dimensions along which digital distribution model innovation can be sought are:
- Digital Disintermediation. Digital technology facilitates real-time communication that is easy and interactive, allowing parties to skip links in the distribution chain, connecting producers and users more directly. So, can some of your middlemen be cut out? E.g.:
- Direct Sourcing. Buying straight from the producer, bypassing importer or wholesaler?
- Direct Marketing. Communicating immediately with the user, avoiding media or agents?
- Direct Sales. Selling straight to the user, skipping dealers and retailers?
- Digital Intermediation. Digital technology also allows for new intermediaries and entirely new channels to emerge, that connect producers to users online in more efficient and/or effective ways. So, can you create a new middleman? E.g.:
- Webshop. Selling online, offering more choice, convenience, and lower prices?
- Portal. Directing traffic online, providing better overview, insight, and navigation?
- Platform. Matchmaking online, connecting many wants to many needs (see model #2)?
- Digital Transportation. Digital technology has the potential to virtualize many products/services, allowing them to be distributed intangibly via the internet instead of tangibly via vehicles and buildings. So, can you cut out physical distribution? E.g.:
- Online. Making them accessible via a browser, such as newspapers and webshops?
- Downloading. Making them accessible via file transfer, such as e-books and software?
- Streaming. Making them accessible via data feed, such as movies and conferences?
- Digital Immediacy. In the analogue world, getting something somewhere takes effort, but also time. Digitalization has the potential to shorten the time between wanting and getting something, making distribution seem almost instantaneous. So, can you cut out time? E.g.:
- On Demand. Delivering immediately upon request, directly matching real-time need?
- Automated Replenishment. Delivering before request, ensuring adequate stock?
- Predictive Analytics. Delivering before request, anticipating real-time need?
Key Insights
- Digitalization allows for value proposition innovation. The ongoing dispersion of digital technologies is a driving force behind value proposition innovation. The three ‘dials’ that can be turned to innovate are the product model dial (changing the core product/service being offered), the revenue model dial (adapting the way the product is paid for), and the distribution model dial (reinventing the way the product is delivered to the user).
- Digital distribution innovation can be found along four dimensions. There are no fixed digital distribution models from which innovators can choose, but there are four dimensions along which possibilities can be sought: parties in the distribution channel can be cut out (digital disintermediation), or added (digital intermediation), while physical distribution can be reduced (digital transportation), as can time (digital immediacy).
- All digital distribution innovation dimensions have many options. Along each of these four dimensions there are many ways in which distribution can be innovated. Here only some common examples have been given, but many others can be found.
- Most digital distribution innovations combine options on different dimensions. The innovativeness of new distribution models is often enhanced by being novel on more than one dimension at the same time.
- Additional steps for digital business model innovation. Having an innovative digital distribution model is often combined with an innovative product model and revenue model to create an innovative value proposition. This in turn needs to be linked to a supporting activity system and resource base to become a fully developed new business model.
Inspired by this kickstart?
Organizations change and develop constantly. In order to lead strategic processes in the organization in a good way, it is important to have a thorough knowledge of various strategic subjects and to apply this knowledge in your everyday work. In the six-day Masterclass Strategic Leadership, you will gain new knowledge, insights and valuable professional experience.
Read more »
Digital Distribution Model Dial is part 20 of a series of management models by prof. dr. Ron Meyer. Ron is managing director of the Center for Strategy & Leadership and publishes regularly on Center for Strategy & Leadership