Digital Product Model Dial
How can digitalization be used to innovate my products/services?TIAS professor of Strategic Leadership Ron Meyer presents an insightful tool to kickstart your thinking: Digital Product Model Dial.
Key Definitions
A value proposition is a bundle of attractive attributes that an organization offers to entice people to become its customers. Every value proposition consists of a core product and/or service, that is distributed and paid for in a way that customers find appealing.
Digital technologies can be employed to innovate, or even transform, value propositions by changing the nature of the product/service (the product model), the way they are distributed (the distribution model) and the manner by which they are paid (the revenue model).
Conceptual Model
The Digital Product Model Dial is one of the three dials (see below right) that can be turned to create an innovative value proposition. The Digital Revenue Model Dial was discussed in Meyer’s Management Models #4 and the Digital Distribution Model Dial is explored as #20. The Digital Product Model Dial suggests that there is no fixed set of product models from which to choose, but that products and/or services can be reinvented along four different dimensions, separately or at the same time. Each dimension has been formulated as a question, with several common examples mentioned as options to consider.
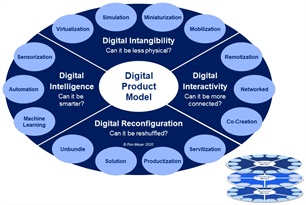
Download picture
Key Elements
The four dimensions along which digital product model innovation can be sought are:
- Digital Intangibility. Digital technology transforms tangible objects and behaviors into coded streams of ones and zeros, freeing products/services from the constraints of needing to be concrete, big, and/or fixed. Can your product be made less physical? E.g.:
- Virtualization. Made entirely intangible, like a digital compass or digital photos?
- Simulation. Turned into a digital model, such as a flight simulator or digital twin?
- Miniaturization. Shrunk in size, like a digital camera or movement sensor?
- Mobilization. Made portable, such as a Bluetooth speaker or projector?
- Digital Interactivity. Digital technology facilitates real-time communication that is easy and interactive, allowing for ongoing cooperation between parties, devices and/or programs, irrespective of distance. Can your product be made more connected? E.g.:
- Remotization. Made to work at a distance, like online surgery or remote monitoring?
- Networked. Made to work together with others, such as taxi booking or online dating?
- Co-Creation. Made together with others, such as customized shoes or joint wikis?
- Digital Intelligence. Digital technology uses data and algorithms to do calculations and make decisions, thus adding intelligence to products/services and supporting and/or replacing human thinking. Can your product be made smarter? E.g.:
- Sensorization. Made to collect data itself, like smart meters and activity trackers?
- Automation. Made to decide itself, like autonomous vehicles or automated answering?
- Machine Learning. Made to learn itself, such as facial recognition or recommendation systems?
- Digital Reconfiguration. By enabling intangibility, interactivity and intelligence, digital technology allows for products/services to be taken apart into various components and/or put together in new ways. Can your product be reshuffled? E.g.:
- Unbundle. Split up, like newspapers lost job search and classified ads?
- Solution. Combined into a package, like smartphones absorbed cameras and diaries?
- Productization. Turned into a product, like travel agency services have become apps?
- Servitization. Turned into a service, like cars are becoming Mobility-as-a-Service?
Key Insights
- Digitalization allows for value proposition innovation. The ongoing development and dispersion of digital technologies facilitates the introduction of new value propositions into the market. The biggest potential impact is on the nature of the core product and/or service being offered (the product model), the way the product is offered to the customer (the distribution model) and the manner in which it is paid for (the revenue model).
- Digital product innovation can be found along four dimensions. There is no fixed set of digital product models from which innovators can select, but there are four dimensions along which innovators can hunt for possibilities: The product can be made less physical (digital intangibility), less disconnected (digital interactivity), less dumb (digital intelligence) and it can be reshuffled (digital reconfiguration).
- Digital product innovation dimensions have many options. Along each of these four dimensions there are many ways in which products can be innovated. Here only some common examples have been given, but many others can be found.
- Digital product innovations often combine options on different dimensions. The innovativeness of new products/services is often enhanced by being novel on more than one dimension at the same time.
- Digital business model innovation requires additional steps. Having an innovative digital product model is often combined with an innovative distribution and revenue model to create an innovative value proposition. This in turn needs to be linked to a supporting activity system and resource base to become a fully developed new business model.
Inspired by this kickstart?
Organizations change and develop constantly. In order to lead strategic processes in the organization in a good way, it is important to have a thorough knowledge of various strategic subjects and to apply this knowledge in your everyday work. In the six-day Masterclass Strategic Leadership, you will gain new knowledge, insights and valuable professional experience.
Read more
Digital Product Model Dial is part 19 of a series of management models by prof. dr. Ron Meyer. Ron is managing director of the Center for Strategy & Leadership and publishes regularly on Center for Strategy & Leadership