How can I map the value-adding activities carried out in my organization? TIAS professor of Strategic Leadership Ron Meyer presents an insightful tool to kickstart your thinking: Activity System Dial.
Key Definitions
To prosper, organizations need to provide products and/or services that are valued by their clients – they must offer a value proposition that prospective customer prefer above all alternatives (see model 38, the Value Proposition Dial).To deliver such a value proposition, organizations need to perform a wide variety of value-adding activities – they must orchestrate a large number of tasks that jointly cost less than the value proposition is worth. Porter (1985) initially called this whole set of tasks the value chain, but later switched to the term activity system, as the activities aren’t necessarily sequential.
Conceptual Model
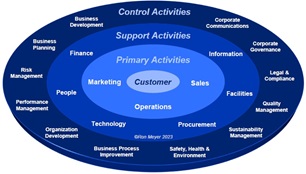
The Activity System Dial provides a map of all potential value-adding activities performed in an organization, structured into three main categories. All activities directly influencing the value perception of the customer, are primary activities. All activities providing resources for running the primary activities (and each other) are support activities and only indirectly impact customers. The remaining activities all seek to steer the primary and support activities in a certain direction, which is why they are called control activities. Over their lifetime, organizations start at the center and then add activities to the outer rings, increasingly further away from the customer’s value experience. The Activity System Dial can be used to plot the existing situation, but also to discuss consistency, balance, and future improvements.
 Key Elements
Key Elements
The three rings of the dial are the following:
1. Primary Activities
As the customer determines what value is, all activities directly impacting the customer’s value perception are called primary. They are ‘wrapped around’ the customer and influence the customer experience at various moments throughout the customer journey. As customer journeys can differ significantly between different types of value propositions, so will the primary activity flow. Marketing tends to focus on the start of the journey, after which products/services are made and then sold, or vice versa, first sold and then made. But in practice, the primary activities tend to be intertwined, with various moments of truth presenting themselves in various orders (e.g., an operational deliver moment, leading to a brand experience moment, leading to a cross-selling opportunity). This is why we speak of an interlinked activity system, not a sequential value chain.
2. Support Activities
In a typical start up, the few employees tend to focus fully on the primary activities, mobilizing the necessary resources on the fly. But soon a need emerges to get someone who can take care of some of the “back-office stuff”, like the people-related infrastructure (HR), finance-related infrastructure (Finance) and information-related infrastructure (IT). This soon leads more resource experts, for procurement (Purchasing), technology (R&D) and facilities. This division of labor allows for specialization, but requires more activity system coordination, while introducing the danger of support activities not fully aligned with primary activity priorities. Note that sometimes the support activities also interact with the customer (e.g., client billing, public facilities, procurement for customers), blurring the boundary between support and primary activities.
3. Control Activities
The third ring of activities doesn’t provide resources, but provides guidance – these activities stipulate policies, determine procedures, shape conditions, and steer behaviors in order to get the best out of the two inner activity rings. In smaller organizations all these control activities tend to be carried out by managers themselves, as they steer performance, risk, quality, planning and sustainability policy. But in larger organizations further specialization takes place, with experts developing rules, templates, and processes, to reach a higher level of professionalization. However, this fragmentation of activities makes it even more important to align all activities in the activity system, while the hazard increases that specialists far away from the customer journey will establish value-destroying regulations and bureaucracy.
Key Insights
• The activity system is about creating customer value. The work that an organization carries out shouldn’t be done because of habit, but because it is the best way to create value for the customer. Therefore, the customer needs to be at the heart of any activity system, with all tasks organized and coordinated around the customer journey.
• The activity system consists of three types of activities. All activities directly influencing the customer’s value perception are primary. All activities focused on providing the resources to run the primary activities (and all other activities) are support activities. All activities steering the primary and support activities (and each other) are control activities.
• The activity system needs to be internally aligned. The activities in all three categories need to be aligned, forming a consistent and balanced system. Support and control activities need to keep customer value at the center and not become self-centered.
• The activity system needs to be strategically aligned. The activity system in turn needs to be aligned with the entire business system, which then need to be attuned to the market system and organizational system (see Strategic Alignment Model, #32).
• The activity system can be mapped and shaped. The Activity System Dial is a framework for mapping an organization’s current activity system but can also be used to design the future activity system, as part of the overall strategy development.
Inspired by this kickstart?
During the six-day Masterclass Organizational Leadership you will work on solutions for a problem of your own definition, such as transforming with your organization and getting employees moving. You will also reflect on the performance of your Management Team and your organization. This will help you realize effective growth for your organization.
Read more about the Masterclass Organizational Leadership »
Activity System Dial is part 50 of a series of management models by prof. dr. Ron Meyer. Ron is managing director of the Center for Strategy & Leadership and publishes regularly on Center for Strategy & Leadership.
:quality(90))
:quality(90))